Name: Rinkal D. Jani
Roll No: 21
Batch: 2016-18
SEM: 4
Enrollment no: 2069108420170012
Paper No 13: The New literature
Topic: Julian Barnes "sense of an ending as a postmodern novel"
Submitted to: Dr Dillip Barad
Department of English,
Smt. S. B. Gardi
Maharaja Krishnakumarsinghji Bhavnagar University
About the Author:

Julian Barnes is an ironist, a post-modern fiction writer and literary critic who occasionally moonlights in the crime and mystery genre. Julian Barnes is a contemporary English writer of Postmodernism in literature. He was more famous for his prosaic style, who was born in Leister on 19 January 1946 and was educated at the city of London school and magladen college Oxford.
He has written crime fiction under the pseudonym Dan
Kavanagh. His brother, Jonathan Barnes, is a philosopher specialized in ancient
philosophy. After working as a lexicographer on the oxford English dictionary,
he began a career as a journalist, reviewing for the Times
Literary supplement and
became a contributory editor for the New
Reviewin 1977.He was assistant literary
editor and television critic for the New
statesman Magazine (1977-81)
and deputy literary editor for the Sunday Times.
Barnes prose is elegant,
witty and playful, and he often employs techniques associated with postmodern
writing unreliable narrators, a self-conscious linguistic style, an inter-textual
blending of different narrative forms-which serve to foreground the process of
literary creation, The gap between experience and language and subjectivity of
‘truth’ and ‘reality’. However, despite this playful experimentation with
language, style and fiction and Form Barnes fiction is also foregrounded
in psychological realism and his themes are serious poignant and we can say
that Heart-felt. He frequently addresses the nature of love, particularly its
dark side, exploring humankind’s capacity for jealousy, obsession and
infidelity.
His
exceptional works are
As a postmodernist writer he
has written some wonderful postmodern novel which is Flaubert's Parrot, apart from this there are
some other works in which we may find the postmodernist twist or witting style,
like in “Sense of an ending”. The Sense of an Ending is no exception to the
rule when it comes to Booker Prize winners being very post-modernist in style.
Winner of the 2011 edition, Barnes’ book does not read like a normal, classic
story. The plot itself is very original, as Barnes crushes stereotypes and
places plot twists in areas where we would expect to see clichés. The finale
besides is a superb example of post-modernist literature. So let’s have a Bird
eye view on “Sense of an ending
as a Postmodernist novel”

What is postmodernism?
as a Postmodernist novel”
What is postmodernism?

The basic difference between the two crucial isms, i.e., Modernism and postmodernism. Modernism believes in holding a center, an authority; whereas Postmodernism rejects the notion of holding a center and hence things fall apar. The term ‘Postmodern seems odd itself, paradoxically evoking what is after (post) the contemporary (modern). The prefix ‘post’ means after, and ‘modern’ can be taken to mean current or up-to-date. But how is it possible to be after and modern at the same time? The structure of the word ‘postmodern’, therefore does not lead to any meaningful definition. Strictly speaking, the postmodern should be thought of as a term of periodization: the postmodern challenges us to see the present in the past, the future in the present, and the present in a kind of no-time.
Postmodernism
queries every aspect of what is known as realism. It presents the world with no
assured and fixed facts. Certainty is replaced by uncertainty. From the
postmodernist perspective, age is cut from the past traditional values as it is
rather preferable to doubt and suspect everything than certitude and
conviction. Everything has melted into destruction (Pritam 42). Postmodernism
adopts Jacques Derrida’s idea of deconstruction 3 which does not mean
destruction; yet it refers to firmness and veracity opposition, as it is
explained by Mowery “It [deconstruction] does not mean destruction, but rather
it is a critique of the criteria of certainty, identity, and truth.” (622) the
theory of postmodernism is based on its refusal that there is no complete
explanation to things because human knowledge is incomplete and fragmented due
to subjective conditions such as facts that result from emotions which make
them changeable and unstable (Mulley 10). Mowery hints that postmodernists are
concerned with “being self-conscious, experimental and ironic.” (615) further,
he emphasizes that they are fascinated by “imprecision and unreliability of
language and with epistemology, [and] the study of what knowledge is.” (615),
that is to say, the language being used is inaccurate and untrustworthy and
knowledge is put under question.
The web of words
postmodernism creates to establish itself is: fragmentation, hybridity,
relativism, play, parody, pastiche, an ironic, anti-ideological stance etc. which
makes a proper context for it, if not a proper definition. Postmodernism,
therefore, can be understood in terms of its seven defining principles: no
truth, no reality, only images, no meaning, multiplicities, equal
representation, and total doubt.
The Postmodern elements which
these writers trace out for their practice are mainly plurality, detachment as
well as the intertextual elements; which help in creating a significant
narrative considerable for the Indian terrain. This concept of finding an alternative
out of the isms has started becoming notable as Alter modernism
Postmodernism borrows from
modernism disillusionment with the givens of society; a penchant for irony; the
self-conscious “play” within the work of art; fragmentation and ambiguity; and
a distracted, decentered, dehumanized subject. But while modernism presented a
fragmented view of human history (as in Eliot’s The Waste Land – [1925]), this fragmentation
was seen as tragic. Despite their pessimism, modernist works still hope,
following Matthew Arnold a generation before, that art may e able to provide
the unity, coherence, and meaning that has been lost in most of modern life, as
church and nation have failed to do. One can locate this hope, faint as it
sometimes is, in such memorable passages as the Molly Bloom section that
closes Joyce’s Ullysses (1922). In contrast, postmodernism not only does not mourn the loss
of meaning but celebrates the activity of fragmentation. Whereas modernism
still seeks a rational meaning in a work of art,
Postmodern Fiction
[Postmodernism]
stems from a recognition that reality is not simply mirrored in human
understanding of it, but rather, is constructed as the mind tries to understand
its own particular and personal reality. For this reason,
postmodernism...focuses on the relative truths of each person. In the
postmodern understanding, interpretation is everything; reality only comes into
being through our interpretations of what the world means to us individually. Thus,
postmodern literature examines through its narratives the nature of knowledge,
both deconstructing established beliefs and purporting new interpretations.
Characteristics of postmodernist Fiction/Writing
Postmodernism
is the philosophical proposal that reality is ultimately inaccessible by human
investigation, that knowledge is a social construction, that truth-claims are
political power plays, and that the meaning of words is to be determined by
readers not authors. In brief, postmodern theory sees reality as what
individuals or social groups make it to be. Retrospective narrative
 Intertextuality
Intertextuality Metafiction
Metafiction Pastiche
Pastiche Minimalism
no
Minimalism
no Irony
playfulness, black humor
Irony
playfulness, black humor Hyper
reality
Hyper
reality Paranoia
Paranoia Fragmentation
Fragmentation Late
Capitalism
Late
Capitalism Subtlety
Subtlety Pretentious
Pretentious Juxtaposition
Juxtaposition Fragmentation
Fragmentation Discontinuity
Discontinuity Inability of Face the Real World
Inability of Face the Real World Ambiguity
Ambiguity No proper Beginning as well proper ending
No proper Beginning as well proper ending
There are several characteristics of
postmodernism are found in Barnes “sense of an ending” and some Postmodernist narrative
techniques through that we can say that Barnes text is as postmodernist novel. It
has the characteristics of a postmodern text. The characteristics of a
postmodern text are Intertextuality, juxtaposition, fragmentation,
discontinuity, inability to face the real world and ambiguity.
The Sense of an Ending has Intertextuality. Intertextuality means the echo of one text into another. Intertextuality usually uses devices like an epigraph. Though this novel does not have an epigraph, its title is taken from Frank Kermode’s book The Sense of an Ending: Studies in the Theory of Fiction. Kermode’s book aims to make sense of the way human beings try to make sense of their lives. The Sense of an Ending echoes the theme of Kermode’s book. The protagonist of this novel, Tony Webster, tries to make sense of the lives of his and his friends.
The Sense of an Ending has juxtaposed past and present of Tony’s life. For example, after getting the photocopy of his letter to Adrian and Veronica, the aged Tony feels guilty for not accepting their relationship and for writing such hurtful words in his youth. Tony says-
“All I could plead was that I had been its author then, but was not its
author now’ (Barnes 91).
This juxtaposition shows how a
person’s view of life changes with time and age. It also shows how a person’s
past has an influence over his present.
The Sense of an Ending is fragmented. The events of the novel are not chronologically told. These are presented in a disjointed way through the stream of consciousness style. For example, in part ‘One’, the narrator tells that Veronica does not dance, but in part ‘Two’, he tells that Veronica has danced with him. Again, in part ‘One’, the narrator tells that he has seen the Seven Bore without Veronica, but in part ‘Two’, he tells that Veronica has been with him in that event.
“I’m not very interested in my school days, and don’t feel any nostalgia
for them (Barnes 4).”
The above line shows that Tony tries
to escape from the reality that his friend Adrian is dead by repressing the
memories. Again, Tony’s clique used to wear their watches with the face on the
inside of the wrist. This shows that they have tried to escape time or reality.
The Sense of an Ending has ambiguity. For example, the novel does not reveal what Adrian has written in his diary after
“So, for instance, if Tony: (Barnes 81)”.
Tony as
well as the readers is not sure whether Adrian has blamed Tony for his
situation and suicide like Veronica or not. There is also an ambiguity about
the reason why Veronica’s mother dislikes her so much to destroy her love
relationships.
As mentioned above, The Sense of an Ending is an apt example of post-modernist literature. As such, certain parts of the story tend to be elusive, hence engaging the author to imagine what could have happened in the plot holes. Moreover the subtlety with which Barnes crafted the story is laudable. All key moments are input in the story, yet they are so subtle that one might not pay enough attention to them. If you’re an admirer of post-modern fiction, then you might end up liking The Sense of an Ending very much.
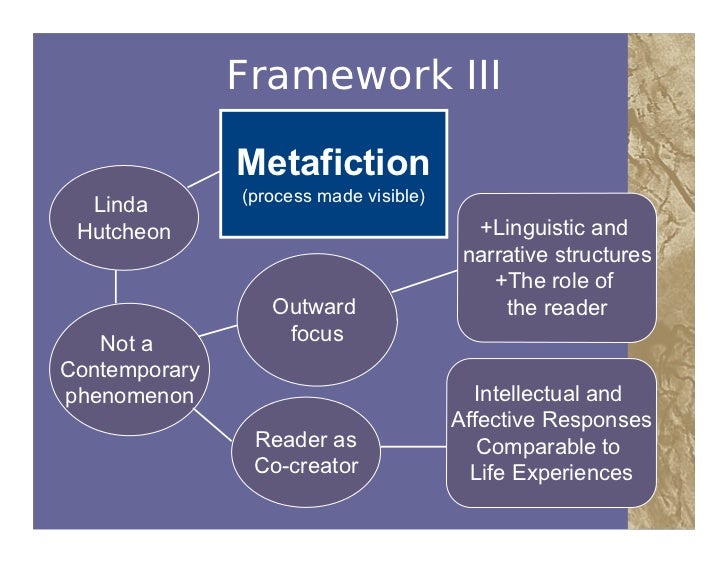
Meta fiction
Meta fictional novels often end with a choice of ending [o]r...with a
sign of impossibility of endings.” ‘sense of an ending is often open for
interpretation, there is not clarity of things like what is the happy ending? What
happened with veronica, does Adrian really is died or still alive, many kinds
of interpretation are opend. There is no clear cut end to the novel. Contemporary writings, in which meta fiction
is used, are deemed to give a sense about reality as being provisional and a
world that no longer contains a fixed veracity , only constructed artifices.
The perception of reality maybe questioned through met fictional devices. Also
memory or truth or social assumptions can be challenged. The question of
identity can be raised. The reader’s assumptions maybe undermined. As a
literary device meta fiction lends itself to many superb extra opportunities
for the writer who is prepared to take a chance or two: for example the text
might become unreliable, or incomplete, or deniable by other characters. It is a
powerful and compelling technique. (01) Metafiction is a tool that can help in
questioning reality. The assumptions that are made by individuals as well as
identity can be challenged and all the postulations that are made by readers
can be then destroyed and any text may be apt to be disbelieved, denied or
incomplete as Barnes write here that
“We live
with such easy assumptions, don't we? For instance, that memory equals events
plus time. But it's all much odder than this. Who was it said that memory is
what we thought we'd forgotten? And it ought to be obvious to us that time
doesn't act as a fixative, rather as a solvent. But it's not convenient--- it's
not useful--- to believe this; it doesn't help us get on with our lives; so we
ignore it.”
― Julian Barnes, The Sense of an Ending
― Julian Barnes, The Sense of an Ending
Incomplete
in the sense that Barnes novel with the quote that “There is responsibility. And beyond
these, there is unrest. There is great unrest” There is no completeness.

Postmodernist narratives
What characterized the postmodernist story line is that “it is marked by a tendency to question the legitimacy of the narrative itself, the refusal to offer any universal truths and multiple points of view.” (Sim 10) There can be noticed also that as postmodernist writers are dubious about certainties; they no longer trust ideas of completion and wholeness which are aspects associated to traditional stories. Therefore, they rely on different ways for structuring narrative, the so called the multiple-ending in which closure is not advocated stands as an example. Postmodernists; however, insist on providing numerous probable results for the plot (Sim 174). Postmodernist novels are interested in the technique of telling4 rather than showing5 , as it is stated by Malpas “Many techniques such as frame narratives, ontological indeterminacy and unreliable narrators […] were identified as crucial to the postmodernism.” Postmodernist narrators are characterized then by complexity and their unreliability is deliberate and results from false ideas.
Bentley Nick (2008) referred
to one of the most prominent features of postmodernism that is its suspicion
towards grand narratives such as the idea of history and truth. Other scholars
such as Sim Stuart (1998), James F. English (2006) and Chalupský Petr (2009)
agreed that postmodernist literary works were interested in the theme of the
past, re-calling and re-telling it through individuals’ retrospect. Hutcheon
Linda (1988) and Bentley Nick (2008) gave less importance to the ultimate
truth; they did not care about the truth itself; however, what mattered
for them was the source of the truth and where it comes from. Truth and history
were no longer taken for granted, they became a moot point and completely
dubious according to the position from where they are told and viewed. In her
2012 academic research, Eva Sràmkovà considered that since postmodernist
writers were suspicious of an absolute and objective truth, they made use of
the unreliable narrator literary device and memory as a way to explore the
narrator’s incredibility and untruthfulness. Additionally, Chalupský Petr
(2009) argued that in contemporary fiction, unreliable narrators are not
motivated by the urge to depict reality as it was but rather as it could have
been through the use of subjectivity and imagination.
A storyteller is neither supposed to be completely true nor
is the reader compelled to believe all that he says “the narrator’s role is to
tell us what is true in the story, and, like tellers in real life, she may have
it wrong, or wish to tell us other than what she believes is true.” (Curries
20) First-Person Narrative-
In postmodern technique most of the time this narrative technique is being
used. Retrospective narratives are often intended to evaluate the
past as pointing to ethical issues. However, narrators are not always reliable;
as they cannot be fully trusted when revealing the truth; mainly when this
supposedly truth is told from a personal perspective.
Unreliable Narrator
The narrator who narrates a story is not always reliable.
Sometimes he may intentionally distort the events in the story and gives false
impressions to the reader. Or he may be lacking in the ability to depict the
events as they happen and unintentionally give the reader inaccurate accounts
of the events (54). An
unreliable narrator typically displays characteristics or tendencies that
indicate a lack of credibility or understanding of the story. Whether due to
age, mental disability or personal involvement, an unreliable narrator provides
the reader with either incomplete or inaccurate information as a result of
these conditions If an author wants intense sympathy for characters who do
not have strong virtues to recommend them, then the psychic vividness of
prolonged and deep inside views will help him. If an author wants to earn the
readers’ confusion, the unreliable narration may help him (377-378). While
Booth considered that one of the functions of an unreliable narrator is to
bring the sense of bewilderment, Bushnell and Lodge viewed it from a rather
different angle that is to increase a noticeable difference between what the
character reckons and believes in and what the reader considers to be true; in
other words, there is a gap between what people think they see and what the
truth really is which is often misreported by them and this is a reader-task.
When the narrator “is discovered to be untrustworthy”, as it has been mentioned
by Booth “then the total effect of the work he [the reader] relays to us is
transformed.” (158) the text that is being read is then apt to be completely
modified.”
“I REMEMBER, IN NO PARTICULAR ORDER
So novel starts with this sentence where he/narrator(Tony)Confesses that whatever he is going to tell his reader is outcome of his broken memory because of that wherever he finds some dots are missing ,he has added his own respective and imagination in his narration. So for me he is classified unreliable narrator. Tony Webster is the unreliable narrator as he himself confesses that some of the incident he does not remember properly. He convinced audience that history is the documentation, neither of winner nor of defeated rather it is the description of lay man so how one can rely on that past. Last part and his own words in the novel prove him unreliable. As he revels the secret of Adrian, Sarah and Veronica. Thus we can say that Tony is an unreliable narrator. Barnes use of an unreliable narrator in order to understand the boundaries, limitations, and possibilities of human relationships. Apart from that there is some quotations which may justify that Unreliable narration in the novel
So novel starts with this sentence where he/narrator(Tony)Confesses that whatever he is going to tell his reader is outcome of his broken memory because of that wherever he finds some dots are missing ,he has added his own respective and imagination in his narration. So for me he is classified unreliable narrator. Tony Webster is the unreliable narrator as he himself confesses that some of the incident he does not remember properly. He convinced audience that history is the documentation, neither of winner nor of defeated rather it is the description of lay man so how one can rely on that past. Last part and his own words in the novel prove him unreliable. As he revels the secret of Adrian, Sarah and Veronica. Thus we can say that Tony is an unreliable narrator. Barnes use of an unreliable narrator in order to understand the boundaries, limitations, and possibilities of human relationships. Apart from that there is some quotations which may justify that Unreliable narration in the novel
“I can’t be sure
of the actual events anymore; I can at least be true to the impressions those
facts left. That’s the best I can manage”

Theorists believe that history does not mean the past, it rather means a narrative that is based on documents and reports that are produced in the past (Nicol 99). As Tony Webster narrating his story with the help of his past memory and documents like Adrins Diary’s page and Mrs. Sarah fords last will. Thereby, one of the features of postmodernism is called historiographical metafiction which refers to the limits of humans’ attempts to know about the past and have an access to it for the simple reason that all that is available in the present time is no more than textual documents. Postmodernism raises questions about how the past is constructed as it doubts and suspects its authenticity (Selden 200). It is believed that the gap that exists between the commonly named real past and its representations is never connected and cannot be bridged and that is mainly what boosts and motivates the production of historical novels and increases critics about them (ibid, 103).As it is quoted in sense of an ending
“History is that certainty
produced at the point where the imperfections of memory meet the inadequacies
of documentation.”
In a
postmodernist age, realism and values to morality are no longer given because
these are meant to be the product of human thoughts only. Lyon qtd. In Pritam
elaborated what is involved here by saying “All that is solid has melted into
air, that reality and morality are not givens but imperfect human constructs.”
(42) In other words, reality is meant to be reflected not only according to the
understanding of humans of it but also to the way it is constructed in that
mind which tries to comprehend it, as it is demonstrated by Somatkar “reality
is not simply mirrored in human understanding of it, but rather, is constructed
as the mind tries to its own particular and personal reality.” (59) These
aspects and many others have been found in art and literature because these
fields in particular have been influenced by the postmodernist trend. In sense
of an ending
“What you end up remembering
isn't always the same as what you have witnessed.”
At the first part Tony Webster
had created a lies about himself. He only narrates the constructed truth about
himself that he is an innocent, No one Knows the real truth about Robson an
Adrian’s suicides It all were constructed truths. Even why Mrs. Sara left some
money for Tony that is also a constructed truth, we don’t know the reality.
“I know this much: that there
is objective time, but also subjective time, the kind you wear on the inside of
your wrist, next to where the pulse lies. And this personal time, which is the
true time, is measured in your relationship to memory.”
― Julian Barnes, The Sense of an Ending
What we believe that later on becomes our truth whether it is really happens or not that we don’t know.
― Julian Barnes, The Sense of an Ending
What we believe that later on becomes our truth whether it is really happens or not that we don’t know.
Postmodern crisis of historical understanding :.
Postmodern culture and a concurrent concern with the irony
and cynicism typical of postmodern literary engagement with historical narrative
. Equally aware of its own inescapable proximity to the postmodern age, the
novel extends a set of postmodern techniques and concerns into a twenty-first
century historiography whilst, at the same time, offering a rebuke, a
rethinking, of these techniques. Barnes’ novel achieves a concerted exploration
of the possibility of situating the personal history of a life, bound up as it
is in memory, within objective, chronological time; an exploration that
suggests the possibility, through a certain attention, a ‘tuning in’ to the
workings of memory, of thinking beyond postmodern relationships to history and
time.
“I thought of the things that
had happened to me over the years, and of how little I had made happen.”
― Julian Barnes, The Sense of an Ending
― Julian Barnes, The Sense of an Ending

“The Sense
of an Ending” Title is connected with the postmodernist idea .Postmodernism
itself invokes innumerable definitions, depending on the field and the scholar.
Julian Barnes‘s work, ranging from
novels with a traditional narrative, to novels that defy convention, to short
stories and essays, experiment with themes and forms which prove that he is,
ultimately, worthy of study, and an author to whom readers should look with
greater seriousness and academic interest. Barnes has often been categorized as a
postmodernist, and an exploration of what, exactly, that term contains is a
useful point to begin a discussion of how his texts function. Here we find further evidence of Barnes‘s
departure from postmodernism.
Conclusion:
Much of the
postmodern writings illustrate the alienation of the individuals and
meaninglessness of human existence. “Postmodernism has proved to be a
snake-like concept whose twists and coils are difficult to pin down ”(Woods 6).
So, time in postmodern novels is measureless and infinite, indicating new time
and new reality . We ”now inhabit a new sort of reality- the postmodern world”
… “Postmodernism refers to the non-realistic and non-traditional literature” ( Hawthorn 83). Apart from that Trivia is beauty of postmodernism, which also very well used by the Julian Barnes.
Post-modernism in a book is a double-edged sword. Some people are mesmerized by the style and revel in reading the story while others can be frustrated with the
author’s unconventionality. For instance, The Sense of an Ending is deemed by many as pretentious, for they reckon that the tending doesn’t make up for the plot holes deliberately placed by the author. Such readers are left unimpressed by Barnes’ peculiar approach to the story and disappointed with the book, as much of the its beauty lies in its style. Julian Barnes gives the touch and Fragment of postmodernism in his Booker prize winning Novel “The sense of an ending”. Though its directly not seems as a postmodernist novel but in a deep level it is as Postmodernist novel. As I considered.
… “Postmodernism refers to the non-realistic and non-traditional literature” ( Hawthorn 83). Apart from that Trivia is beauty of postmodernism, which also very well used by the Julian Barnes.
Post-modernism in a book is a double-edged sword. Some people are mesmerized by the style and revel in reading the story while others can be frustrated with the
author’s unconventionality. For instance, The Sense of an Ending is deemed by many as pretentious, for they reckon that the tending doesn’t make up for the plot holes deliberately placed by the author. Such readers are left unimpressed by Barnes’ peculiar approach to the story and disappointed with the book, as much of the its beauty lies in its style. Julian Barnes gives the touch and Fragment of postmodernism in his Booker prize winning Novel “The sense of an ending”. Though its directly not seems as a postmodernist novel but in a deep level it is as Postmodernist novel. As I considered.
Works Cited
Kainzow. "Why you should read ‘The Sense of an
Ending’ (J.Barnes)." Why you should read ‘The Sense of an Ending’
(J.Barnes). 23 04 2015.
Paynel, Oliver. "History and the Claims of
Memory in Julian Barnes’ The Sense of An Ending." Stet Home an online
postgraduate research journal 4 (n.d.).
Rayhane, Hourari. The Use of the Unreliable
Narrator in Postmodernist British Novel: Ian McEwan’s Atonement (2001) and
Julian Barnes’ The Sense of an Ending (2011). 15 11 2016. 06 04 2018.
‘
No comments:
Post a Comment